Whole Person Health: What It Is and Why It's Important
What is whole person health?
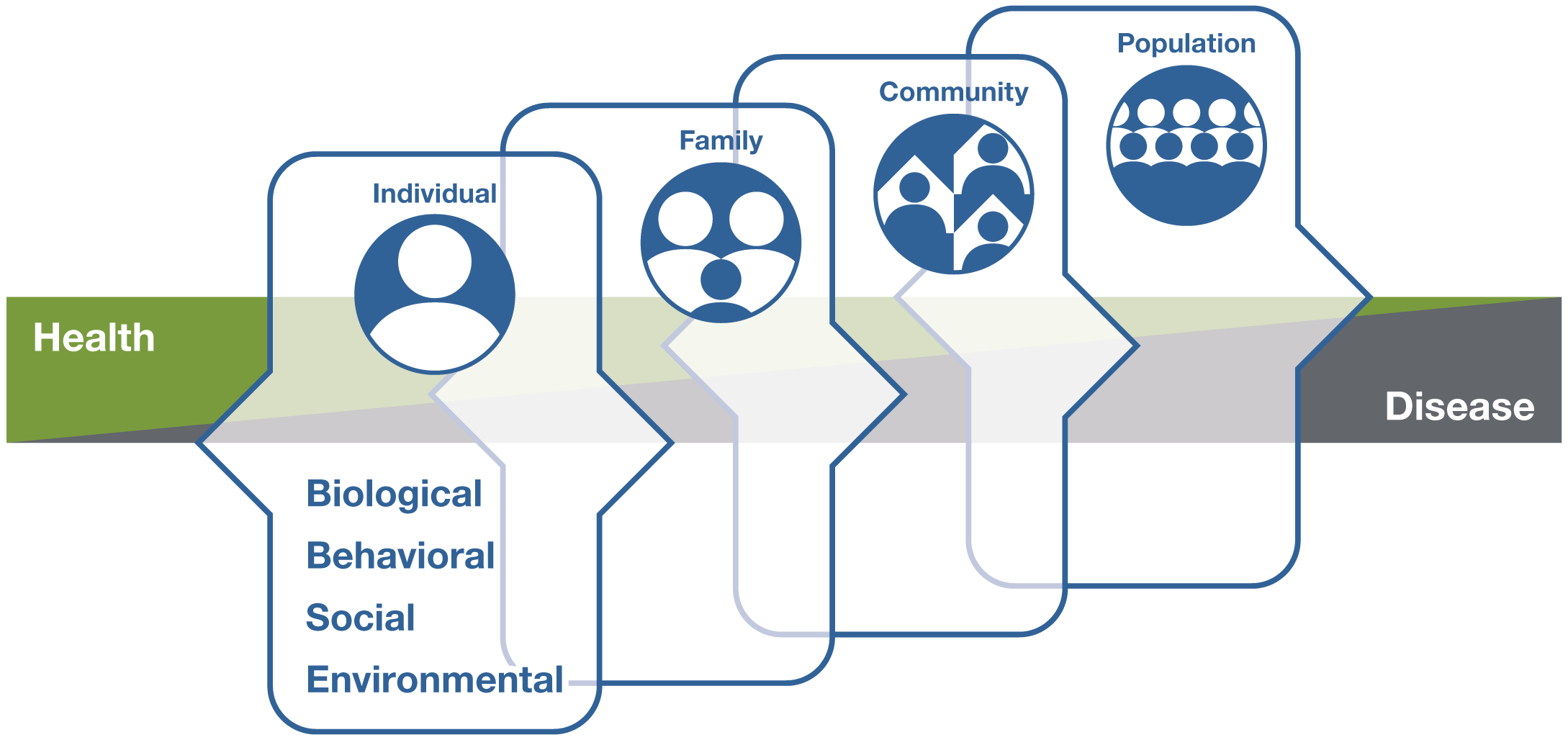
Whole person health involves looking at the whole person—not just separate organs or body systems—and considering multiple factors that promote either health or disease. It means helping and empowering individuals, families, communities, and populations to improve their health in multiple interconnected biological, behavioral, social, and environmental areas. Instead of just treating a specific disease, whole person health focuses on restoring health, promoting resilience, and preventing diseases across a lifespan.
Why is whole person health important?
Health and disease are not separate, disconnected states but instead occur on a path that can move in two different directions, either toward health or toward disease.
On this path, many factors, including one’s biological makeup; some unhealthy behaviors, such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, chronic stress, and poor sleep; as well as social aspects of life—the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age—can lead to chronic diseases of more than one organ system. On the other hand, self-care, lifestyle, and behavioral interventions may help with the return to health.
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and degenerative joint disease, can also occur with chronic pain, depression, and opioid misuse—all conditions exacerbated by chronic stress. Some chronic diseases increase the immediate and long-term risks with COVID-19 infection. Understanding the condition in which a person has lived, addressing behaviors at an early stage, and managing stress can not only prevent multiple diseases but also help restore health and stop the progression to disease across a person’s lifespan.
Is whole person health being used now in health care?
Some health care systems and programs are now focusing more on whole person health.
U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health Approach
The VA’s Whole Health System of Care and Whole Health approach aims to improve the health and well-being of veterans and to address lifestyle and environmental root causes of chronic disease. The approach shifts from a disease-centered focus to a more personalized approach that engages and empowers veterans early in and throughout their lives to prioritize healthy lifestyle changes in areas like nutrition, activity, sleep, relationships, and surroundings. Conventional testing and treatment are combined with complementary and integrative health approaches that may include acupuncture, biofeedback, massage therapy, yoga, and meditation.
U.S. Department of Defense Total Force Fitness Program
The Total Force Fitness program arose within the U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System in response to the need for a more holistic approach—a focus on the whole person instead of separate parts or only symptoms—to the demands of multiple deployments and the strains on the U.S. Armed Forces and their family members. The focus extends the idea of total fitness to include the health, well-being, and resilience of the whole person, family, community, and U.S. military.
Whole Health Institute
Established in 2020, the Whole Health Institute’s Whole Health model helps people identify what matters most to them and build a plan for their journey to whole health. The model provides tools to help people take good care of their body, mind, and spirit, and involves working with a health care team as well as tapping into the support of family, friends, and communities.
North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services has incorporated a whole person health approach into its health care system by focusing on integrating physical, behavioral, and social health. The state has taken steps to encourage collaborative behavioral health care and help resolve widespread inequities in social conditions, such as housing and nutritious food access.
Ornish Program for Reversing Heart Disease
The Ornish Program for Reversing Heart Disease is an intensive cardiac rehabilitation program that has been shown to reverse the progression of coronary heart disease through lifestyle changes, without drugs or surgery. The program is covered by Medicare and some health insurance companies. The program’s lifestyle changes include exercise, smoking cessation, stress management, social support, and a whole-foods, plant-based diet low in total fat. The program is offered by a team of health care professionals who provide the support that individuals need to make and maintain lasting changes in lifestyle.
What does research show about whole person health?
A growing body of research suggests the benefits of healthy behaviors, environments, and policies to maintain health and prevent, treat, and reverse chronic diseases. This research includes several large, long-term epidemiological studies—such as the Framingham Heart Study, Nurses’ Health Study, and Adventist Health Studies—that have evaluated the connections between lifestyle, diet, genetics, health, and disease.
There is a lack, however, of randomized controlled trials and other types of research on multicomponent interventions and whole person health. Challenges come with conducting this type of research and with finding appropriate ways to assess the evidence. But opportunities are emerging to explore new paths toward reliable and rigorous research on whole person health.
Will the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) fund research on whole person health?
Yes, NCCIH plans to fund research on whole person health. (Details can be found in the NCCIH Strategic Plan FY 2021–2025: Mapping a Pathway to Research on Whole Person Health.)
By deepening the scientific understanding of the connections that exist across the different areas of human health, researchers can better understand how conditions interrelate, identify multicomponent interventions that address these problems, and determine the best ways to support individuals through the full continuum of their health experience, including the return to health.
For More Information
NCCIH Clearinghouse
The NCCIH Clearinghouse provides information on NCCIH and complementary and integrative health approaches, including publications and searches of Federal databases of scientific and medical literature. The Clearinghouse does not provide medical advice, treatment recommendations, or referrals to practitioners.
Toll-free in the U.S.: 1-888-644-6226
Telecommunications relay service (TRS): 7-1-1
Website: https://www.nccih.nih.gov
Email: info@nccih.nih.gov (link sends email)
Know the Science
NCCIH and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) provide tools to help you understand the basics and terminology of scientific research so you can make well-informed decisions about your health. Know the Science features a variety of materials, including interactive modules, quizzes, and videos, as well as links to informative content from Federal resources designed to help consumers make sense of health information.
Explaining How Research Works (NIH)
Know the Science: How To Make Sense of a Scientific Journal Article
PubMed®
A service of the National Library of Medicine, PubMed® contains publication information and (in most cases) brief summaries of articles from scientific and medical journals. For guidance from NCCIH on using PubMed, see How To Find Information About Complementary Health Practices on PubMed.
Website: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Key References
- Aggarwal M, Ornish D, Josephson R, et al. Closing gaps in lifestyle adherence for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology. 2021;145:1-11.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Decision Memo for Intensive Cardiac Rehabilitation (ICR) Program—Dr. Ornish’s Program for Reversing Heart Disease (CAG-00419N). Accessed at https://www.cms.gov/ on April 26, 2021.
- Deuster PA, O’Connor FG. Human performance optimization: culture change and paradigm shift. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2015;29(suppl 11):S52-S56.
- Gaudet T, Kligler B. Whole health in the whole system of the Veterans Administration: how will we know we have reached this future state? Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2019;25(S1):S7-S11.
- Malecki HL, Gollie JM, Scholten J. Physical activity, exercise, whole health, and integrative health coaching. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 2020;31(4):649-663.
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. NCCIH Strategic Plan FY 2021–2025: Mapping a Pathway to Research on Whole Person Health. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health website. Accessed at https://www.nccih.nih.gov/about/nccih-strategic-plan-2021-2025 on May 14, 2021.
- North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services website. Healthy Opportunities and Medicaid Transformation. Accessed at https://www.ncdhhs.gov/about/department-initiatives/healthy-opportunities/healthy-opportunities-pilots/healthy on April 26, 2021.
- Military Health System website. Total Force Fitness. Accessed at https://health.mil/Military-Health-Topics/Total-Force-Fitness on April 26, 2021.
- Tilson EC, Muse A, Colville K, et al. Investing in whole person health: working toward an integration of physical, behavioral, and social health. North Carolina Medical Journal. 2020;81(3):177-180.
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs website. Whole Health. Accessed at https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/ on April 26, 2021.
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs website. Whole Health Library. Accessed at https://www.va.gov/wholehealthlibrary/ on April 26, 2021.
- Vodovotz Y, Barnard N, Hu FB, et al. Prioritized research for the prevention, treatment, and reversal of chronic disease: recommendations from the Lifestyle Medicine Research Summit. Frontiers in Medicine (Lausanne). 2020;7:585744.
- Whitehead AM, Kligler B. Innovations in care: complementary and integrative health in the Veterans Health Administration Whole Health System. Medical Care. 2020;58(9S)(suppl 2):S78-S79.
Other References
- Alborzkouh P, Nabati M, Zainali M, et al. A review of the effectiveness of stress management skills training on academic vitality and psychological well-being of college students. Journal of Medicine and Life. 2015;8(4):39-44.
- Bisht K, Sharma K, Tremblay M-È. Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease: roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Neurobiology of Stress. 2018;9:9-21.
- Buettner D, Skemp S. Blue Zones: lessons from the world’s longest lived. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 2016;10(5):318-321.
- Chen T-L, Chang S-C, Hsieh H-F, et al. Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on sleep quality and mental health for insomnia patients: a meta-analysis. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2020;135:110144.
- Conversano C, Orrù G, Pozza A, et al. Is mindfulness-based stress reduction effective for people with hypertension? A systematic review and meta-analysis of 30 years of evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(6):2882.
- Katz DL, Karlsen MC, Chung M, et al. Hierarchies of evidence applied to lifestyle medicine (HEALM): introduction of a strength-of-evidence approach based on a methodological systematic review. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2019;19(1):178.
- Kruk J, Aboul-Enein BH, Bernstein J, et al. Psychological stress and cellular aging in cancer: a meta-analysis. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2019;2019:1270397.
- Levesque C. Therapeutic lifestyle changes for diabetes mellitus. Nursing Clinics of North America. 2017;52(4):679-692.
- Ni Y, Ma L, Li J. Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy in people with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2020;52(4):379-388.
- Ornish Lifestyle Medicine website. The Ornish Reversal Program: Intensive Cardiac Rehabilitation. Accessed at https://www.ornish.com/intensive-cardiac-rehab/ on April 26, 2021.
- Schneiderman N, Ironson G, Siegel SD. Stress and health: psychological, behavioral, and biological determinants. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 2005;1:607-628.
- Seal KH, Becker WC, Murphy JL, et al. Whole Health Options and Pain Education (wHOPE): a pragmatic trial comparing whole health team vs primary care group education to promote nonpharmacological strategies to improve pain, functioning, and quality of life in veterans—rationale, methods, and implementation. Pain Medicine. 2020;21(suppl 2):S91-S99.
- Tamashiro KL, Sakai RR, Shively CA, et al. Chronic stress, metabolism, and metabolic syndrome. Stress. 2011;14(5):468-474.
- Whayne TF Jr, Saha SP. Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and ischemic heart disease. Current Cardiology Reports. 2019;21(1):1.
- Whole Health Institute website. Accessed at https://www.wholehealth.org/ on May 19, 2021.
Acknowledgments
NCCIH thanks Mary Beth Kester, M.S., and Helene M. Langevin, M.D., NCCIH, for their review of this publication.
This publication is not copyrighted and is in the public domain. Duplication is encouraged.
NCCIH has provided this material for your information. It is not intended to substitute for the medical expertise and advice of your health care provider(s). We encourage you to discuss any decisions about treatment or care with your health care provider. The mention of any product, service, or therapy is not an endorsement by NCCIH.